Architecture
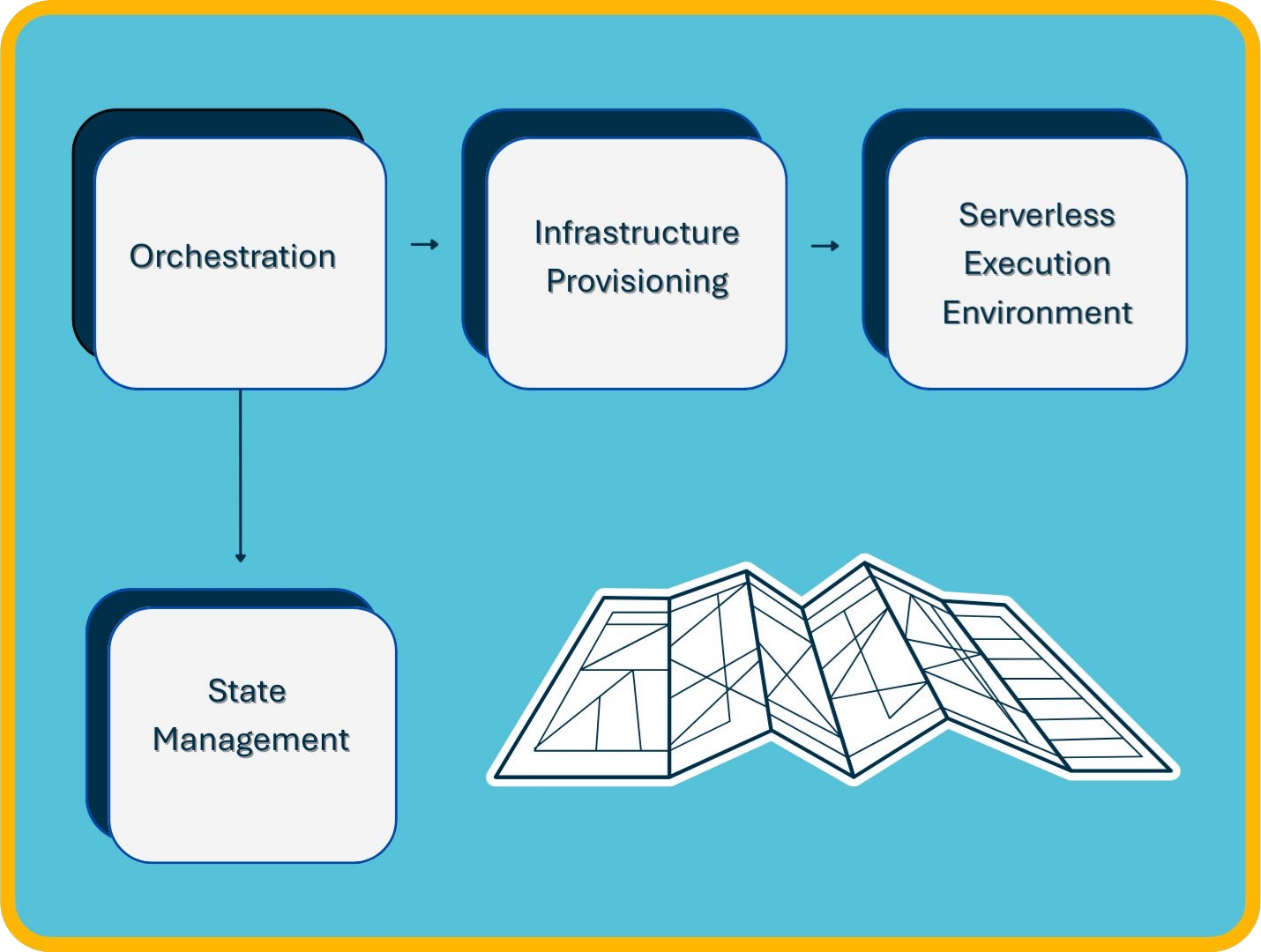
Nimbus utilizes a serverless architecture designed to minimize operational complexity and streamline the deployment of small NLP models. The architecture is organized into three primary components:
- Nimbus CLI: Responsible for user interaction, orchestration, and artifact preparation.
- Cloud Infrastructure (AWS CDK): Responsible for infrastructure definition and deployment.
- Model Serving Runtime (AWS Lambda): Utilized for scalable and isolated model inference execution.
These components work together to automate NLP model serving in a cost-effective, secure, and reliable manner.
To see Nimbus in action please visit our Walkthrough page.
Orchestration - Nimbus CLI
The Nimbus Command Line Interface (CLI) streamlines the deployment experience, abstracting away infrastructure complexities. The CLI is the central orchestration tool for deploying and managing NLP models.

The CLI’s primary responsibilities include:
- Interactive Configuration: Guides users through prompts to collect deployment details (model name, description, source path, and model type).
- Artifact Generation: Prepares standardized runtime artifacts, including inference scripts, dependency lists, Dockerfiles, and models, storing them in a structured local staging directory.
- State Management: Maintains a central configuration file that serves as the authoritative record of deployed models and their metadata.
- Cloud Deployment Invocation: Executes AWS deployments via AWS CDK, triggering cloud infrastructure provisioning based on the current state in the configuration file.
Cloud Infrastructure Provisioning - AWS CDK
Nimbus uses the AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) to define and provision infrastructure as code (IaC), providing reliable and repeatable deployments. The CDK synthesizes CloudFormation templates dynamically based on the state recorded in the local configuration file.
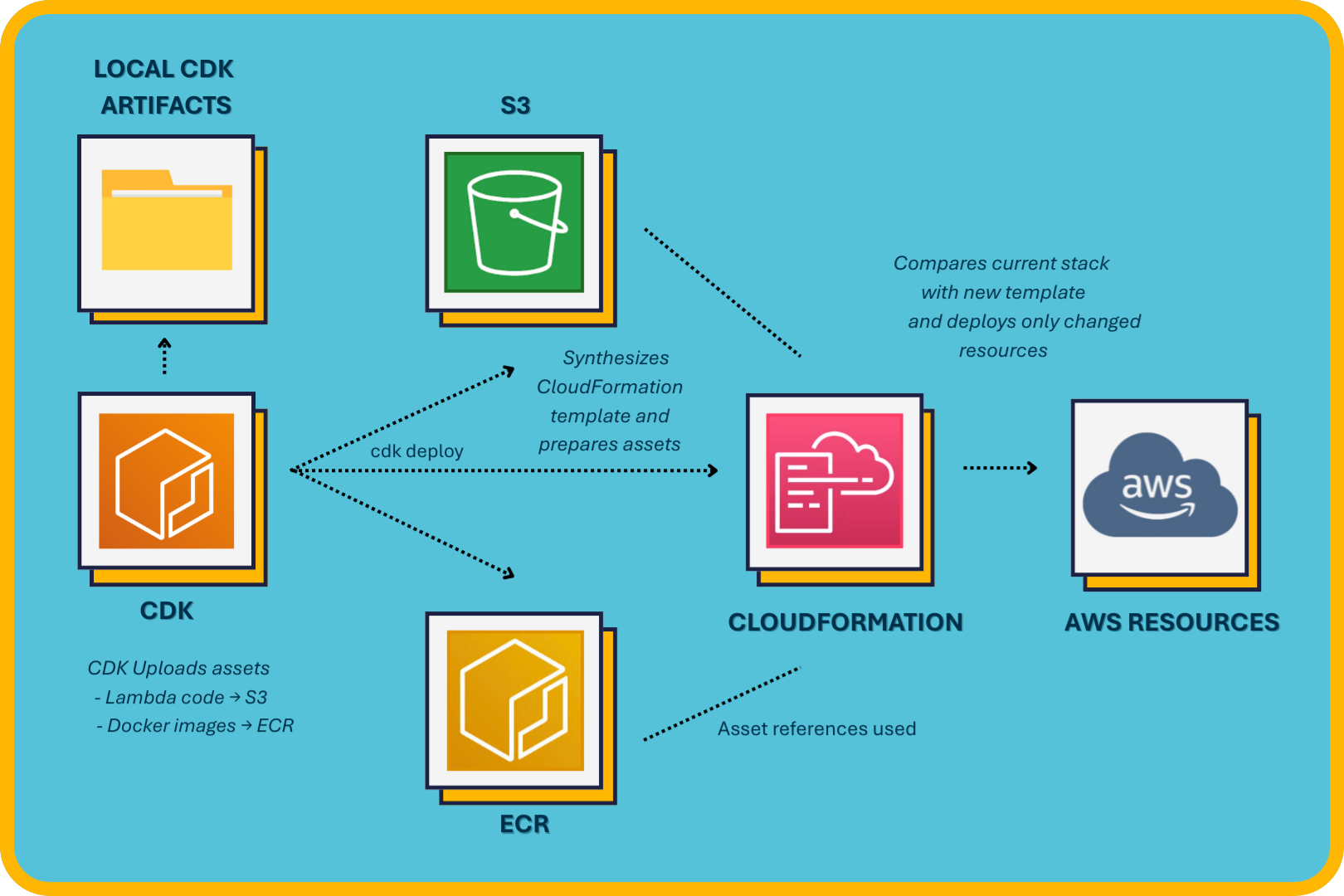
The core AWS resources provisioned by the CDK include:
- AWS Lambda Functions: Each NLP model runs within its own isolated Lambda function packaged as a Docker container. This ensures that models and their dependencies remain fully encapsulated, enabling independent scaling and updates.
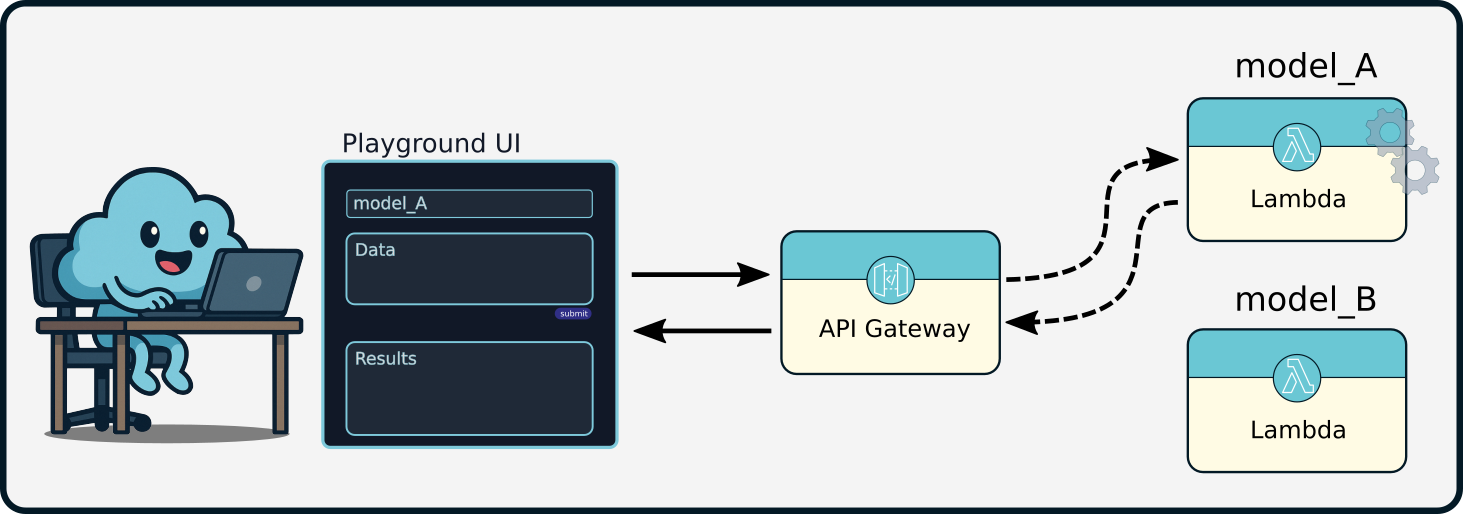
- AWS API Gateway: Serves as the unified HTTP interface, exposing each model through clear, predictable API endpoints. It enforces security and access control via an API key and usage plan.
- Asset Management (ECR & S3): CDK implicitly manages Docker container images in Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) and static deployment artifacts (e.g., CloudFormation templates) in Amazon S3.
When a user initiates a deployment through the CLI, CDK incrementally updates infrastructure based on detected changes in the CloudFormation templates. Only new or modified models trigger resource updates, ensuring efficient deployments.
Model Serving Runtime - AWS Lambda

AWS Lambda functions form the runtime environment for Nimbus deployments, enabling scalable, serverless inference execution. Lambda offers several key benefits aligned with Nimbus’s objectives:
- Automatic Scaling: Lambda automatically handles traffic spikes, scaling model inference workloads without manual intervention.
- Cost-Efficient Compute: Resources are billed per invocation, ideal for the intermittent, low-traffic inference scenarios typical of task-specific NLP models.
- Containerization: Docker-based deployment ensures consistent runtime environments, reducing dependency-related issues between development and production.
A standardized Python runtime script and Dockerfile ensure predictable behavior and consistent results across all deployed models.
Data Flow and Deployment State Management
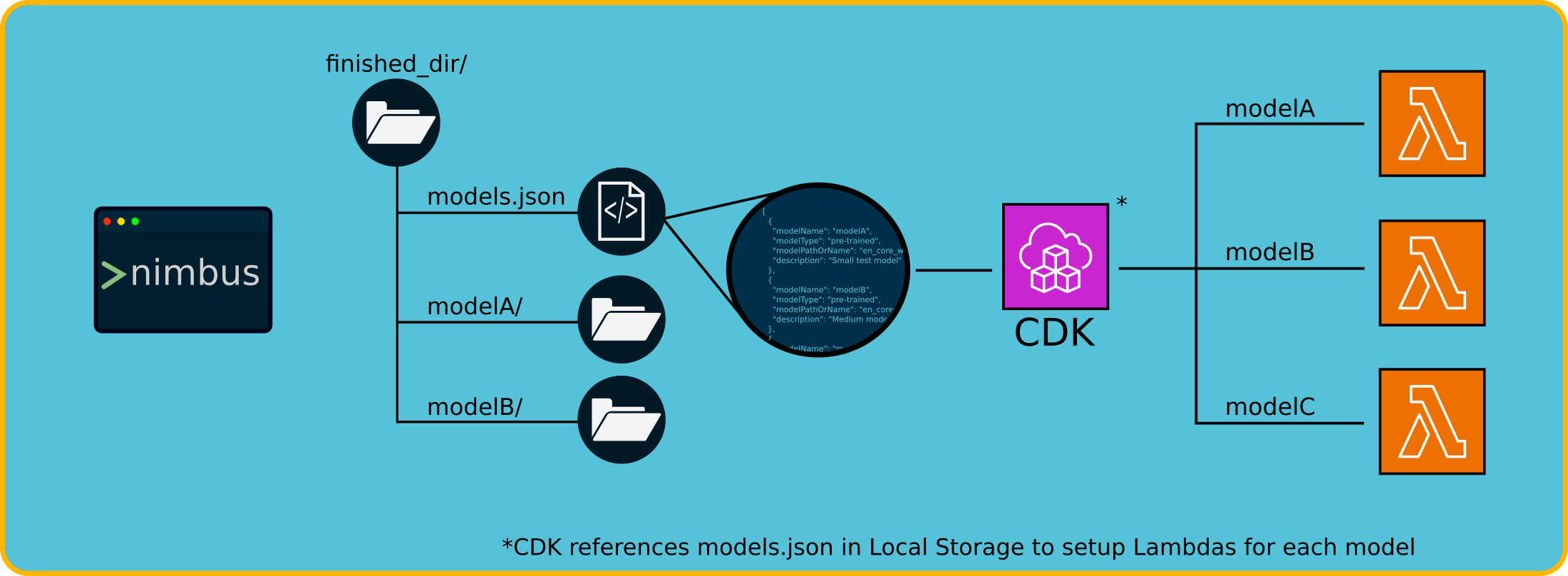
Nimbus maintains deployment state locally through the configuration file stored in the user’s configured artifacts directory, which is created upon first use of the Nimbus CLI. This local file tracks intended deployments and their metadata, forming the source of truth for all deployment operations.
In the cloud, AWS CloudFormation manages actual deployed resource states, providing synchronization between the intended state (as codified in the local configuration file) and the infrastructure state. Users do not need to manage cloud infrastructure manually—CDK automates resource creation, updates, and deletion based on the local state file.
This approach reflects a design choice: on a small team, the focus is on use and accessibility of the models. As a result, there is no operational need to externalize or centralize deployment configurations in the cloud. By avoiding additional cloud services for state management, Nimbus simplifies the overall experience while reducing infrastructure complexity and cost.
For deployed models, prediction requests flow securely from end-users or client applications through API Gateway endpoints to the corresponding Lambda function for inference. After processing, Lambda returns predictions back through API Gateway, completing the cycle.
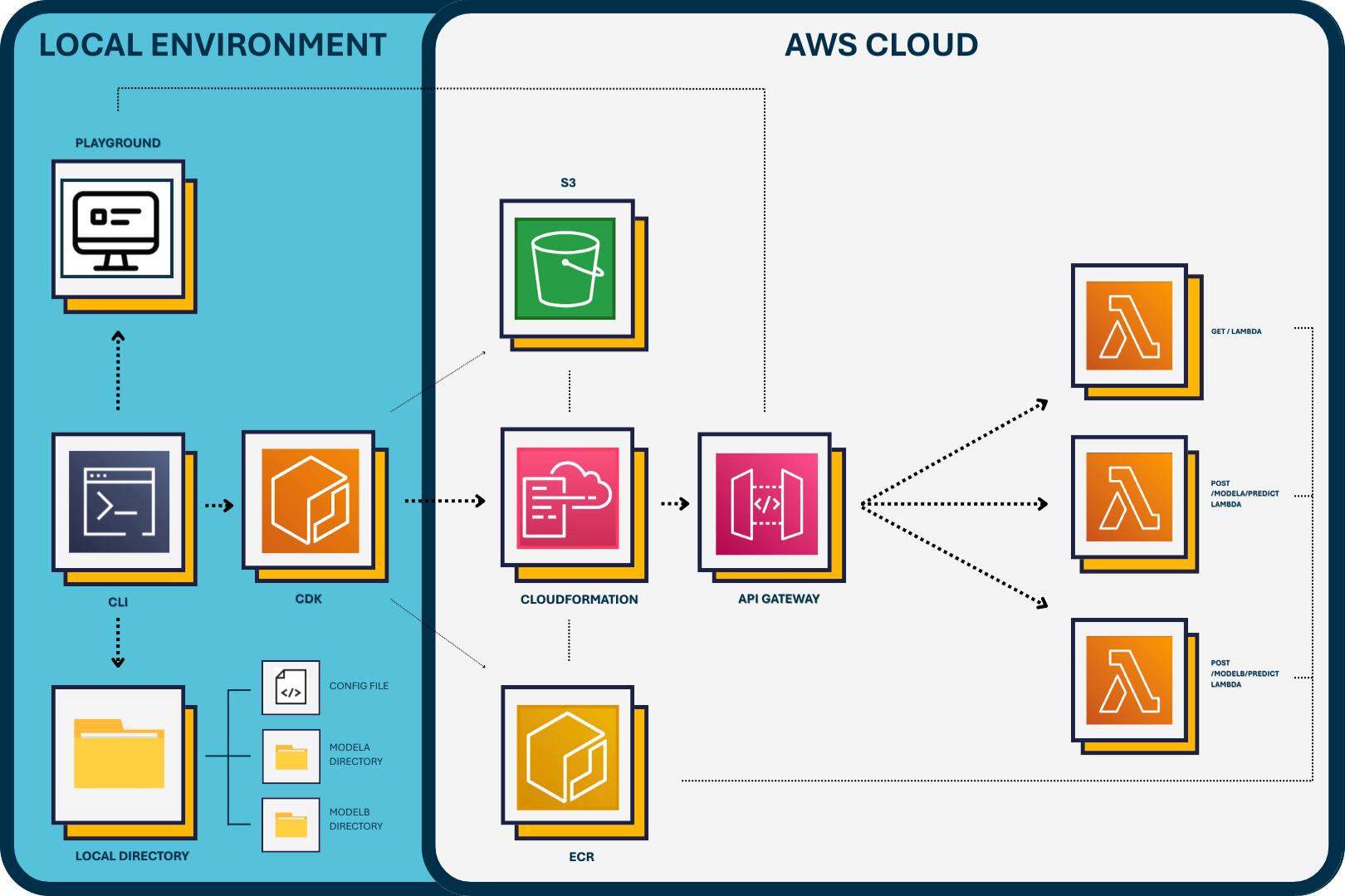
Nimbus UI - Playground
While not a core component of Nimbus’s infrastructure, the Nimbus Playground provides users with a convenient local interface to test deployed models interactively. Launched through the CLI, this lightweight, React-based interface allows quick verification of model deployments and functionality before integration into broader systems or internal workflows.
To see Nimbus in action please visit our Walkthrough page.